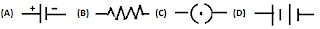Choose Appropriate Alternative
- The SI unit of electric charge is...
[A] ampere [B] volt [C] watt [D] coulomb
- How many electrons will be there in 1.6 C charge?
[A] 1017 [B] 1018 [C] 1019 [D] 1020
- 1 μA = ______ mA.
[A] 10-16[B] 10-3 [C] 103 [D] 106
- Which of the following materials has more number of free electrons?
[A] Copper [B] Glass [C] Rubber [D] Iron
- According to Ohm's law...
[A] The resistance increases with the increase in current. [B] The resistance increases with the increase in voltage. [C] The current increases with the increase in voltage. [D] The resistance and current both increase with the increase in voltage.
- The formula for electric current is...
[A] I = Q.t [B] I = Q/t [C] I = t/Q [D] I = W.t
- 2 A current is passed through a conducting wire for 1 min. How much charge will flow through the wire?
[A] 2 C [B] 30 C [C] 60 C [D] 120 C
- In an electrical appliance, current of 4.8 A is passed. The number of electrons passing through it in 1 sec will be...
[A] 0.33 x 1019 [B] 3.3 x 1019 [C] 3 x 1019 [D] 4.8 x 1019
- Which of the following formulas represents voltage?
[A] Work/(current.time) [B] Work.time/current [C] (Work).(electric charge) [D] (Work).(electric charge).(time)
- The unit of electrical potential difference is...
[A] J [B] J/C [C] J.C [D] C/J
- If the work done to move 3 C electric charge from one point to another
point is 15 J, what will be the potential difference between these points?
[A] 3 V [B] 15 V [C] 5 V [D] 45 V
- The resistance of a conducting wire is 10 Ω. How much electric current will flow by connecting it with a battery of 1.5 V?
[A] 0.15 mA [B] 1.5 mA [C] 15 mA [D] 150 mA
- On which factors does the resistivity of a conducting wire depend?
[A] Length of wire [B] Cross-sectional area of wire [C] Volume of wire [D] Material of wire
- If 5 equal pieces are made from a wire having resistance 5 Ω and then each piece is connected in parallel to others, then their equivalent resistance will be...
[A] 1/5 Ω [B] 1 Ω [C] 5 Ω [D] 25Ω
- The unit of resistivity is...
[A] Ω [B] Ω.m [C] Ω/m [D] m/Ω
- What will be the equivalent resistance between points A and B of the following circuit?
[A] 1 Ω [B] 2 Ω [C] 5 Ω [D] 10 Ω
- What will be the equivalent resistance between points A and B of the following circuit?
[A] 4 Ω [B] 8 Ω [C] 2 Ω [D] ⒠
- What will be the equivalent resistance between points A and B of the following circuit?
[A] 2.5 Ω [B] 5 Ω [C] 12.5 Ω [D] 20 Ω
- Which physical quantity has the unit kWh?
[A] Work [B] Electric power [C] Electric current [D] Electric potential
- 1 kWh = _____ joule.
[A] 3.6 x 106 [B] 3.6 x 103 [C] 3.6 x 10-6 [D] 3.6 x 10-3
- An electric heater consumes 1.1 kW power when 220V voltage is applied to it. How much current will flow through it?
[A] 1.1 A [B] 2.2 A [C] 4 A [D] 5 A
- What makes electric current flow through a solution?
[A] Only free electrons [B] Only positive ions [C] Only negative ions [D] Positive and negative ions
- The distilled water acts as _____ for the electricity.
[A] conductor [B] insulator [C] semiconductor [D] none
- The magnitude of electric force between the charges can be calculated using the law devised by...
[A] Coulomb [B] Ohm [C] Maxwell [D] Ampere
- Free electrons are...
[A] in the first orbit [B] in any orbit [C] valence electrons [D] on the surface of the conductor
- _____ discovered electrons.
[A] Ampere [B] Faraday [C] Thomson [D] Coulomb
- 1 mA = _____ A.
[A] 10 [B] 10-1[C] 10-2[D] 10-3
- In Volta's cell...
[A] electrical energy is converted to thermal energy. [B] thermal energy is converted to electrical energy. [C] chemical energy is converted to electrical energy. [D] electrical energy is converted to chemical energy.
- In Volta's cell _____ plate acts as cathode.
[A] copper [B] graphite [C] zinc [D] aluminium
- The SI unit of resistance is...
[A] coulomb/sec [B] volt/ampere [C] ampere/volt [D] volt/joule
- Which of the following has maximum resistivity?
[A] Tungsten [B] Nichrome [C] Aluminium [D] Diamond
- Which of the following is a semiconductor?
[A] Germanium [B] Diamond [C] Graphite [D] Nichrome
- The chemical equivalent of an atom is the ratio of...
[A] atomic mass to atomic radius [B] atomic radius to atomic mass [C] atomic mass to valency [D] valency to atomic mass
- Work done on an electric charge is stored in it as...
[A] potential energy [B] kinetic energy [C] thermal energy [D] nuclear energy
- _____ is not essential to obtain electric current.
[A] Free electrons [B] Potential difference [C] Electric circuit [D] Potential
- Who invented the simple electrochemical cell?
[A] Faraday [B] Edison [C] Volta [D] Coulomb
- When resistors are connected in series...
[A] voltage drop is uniform [B] current is uniform [C] voltage drop and current are uniform [D] neither of the two is uniform
- When resistors are connected in parallel...
[A] voltage drop is uniform [B] current is uniform [C] voltage drop and current are uniform [D] neither of the two is uniform
- The equivalent resistance of three resistors of 6Ω, 12Ω and 12Ω connected in parallel is...
[A] 6Ω [B] 12Ω [C] 3Ω [D] 1/3Ω
- Which of the following is not correct for electric work(W)?
[A] W = V.Q [B] W = V.I.t [C] W = I2Rt [D] W = I2RQ
- _____ is not a unit of energy.
[A] joule [B] watt [C] watt.second [D] kWh
- 1 joule = ______.
[A] 1 watt.second [B] 1 watt/sec [C] 1 coulomb/sec [D] 1 unit
- Which of the following is not correct?
[A] P = W/t [B] P = I2R [C] P = W.I [D] P = V.I
- Silicon is a/an...
[A] conductor [B] insulator [C] semiconductor [D] superconductor
- The equivalent resistance of the resistances connected in parallel is...
[A] smaller than the smallest resistance [B] larger than the largest resistance [C] an average of all resistances [D] algebraic sum of all resistances
- 1 unit of domestic electrical energy is...
[A] 1 joule [B] 1 watt.sec [C] 3.6 x 106 joule [D] 3.6 x 106kWh
- Three resistances of equal magnitude are connected in parallel. The circuit current is 3 A. Then the current passing through each resistor is...
[A] 3 A [B] 1 A [C] 9 A [D] 1/3 A
- How much total electric charge is present on 100 protons?
[A] 6 x 10-19C [B] 6 x 10-17C [C] 1.6 x 10-19C [D] 1.6 x 10-17C
- Which of the following is a good conductor of electricity?
[A] Rubber [B] Glass [C] Plastic [D] Graphite
- Which of the following is a bad conductor (insulator) of electricity?
[A] Copper [B] Graphite [C] Glass [D] Silver
- Which of the following statements is true for electric current?
[A] The direction of conventional current and that of electrons is opposite. [B] The direction of conventional current and that of electrons is same. [C] The direction of conventional current is random. [D] Electron flow is random.
- 1 μA = ______ mA
[A] 10-1 [B] 10-2 [C] 10-3 [D] 103
- 1 mA = _____ μA
[A] 10-1 [B] 10-3[C] 103 [D] 106
- How many electrons will carry 4.8 x 10-16 C charge?
[A] 300 [B] 3000 [C] 480 [D] 4800
- The unit coulomb/sec is expressed as...
[A] Ampere [B] Volt [C] Ohm [D] Watt
- The SI unit of electric current is...
[A] Ohm [B] Coulomb [C] Ampere [D] Volt
- If the electric charge passing through a conductor in 5 minutes is 480 C, the current flowing through it is...
[A] 96 [B] 2400 [C] 1.6 [D] 2.4
- Which device is used to measure electrical potential difference?
[A] Ammeter [B] Voltmeter [C] Wattmeter [D] Galvanometer
- The SI unit of electrical potential difference is...
[A] Ampere [B] Ohm [C] Weber [D] Volt
- 1.5 C charge is moved from a point at 5 V potential to a point at 8 V potential. What is the amount of work done in joule?
[A] 1.5 [B] 2.0 [C] 3.0 [D] 4.5
- If the work done to move 4 C charge from one point to another point is 10 joule, what is the potential difference between those points?
[A] 2.5 V [B] 40 V [C] 14 V [D] 160 V
- Which of the following is true?
[A] Joule = (volt/coulomb) [B] Volt = (joule/coulomb) [C] Coulomb = (volt/joule) [D] Coulomb = (joule x volt)
- According to Ohm's law...
[A] Current increases linearly with increase in voltage. [B] The current ---> voltage graph is a straight line. [C] The ratio of voltage and current is constant. [D] All three in A, B and C are correct.
- The SI unit of resistance is...
[A] volt [B] volt.ampere [C] ampere/volt [D] volt/ampere
- Which of the following materials has least resistance?
[A] Aluminium [B] Glass [C] Carbon [D] Silicon
- 1.5 A current flows through a resistor when it is connected to a circuit with 3 V potential difference. What is the value of resistance?
[A] 4.5Ω [B] 2Ω [C] 0.5Ω [D] 1.5Ω
- When a 15V battery is connected across a resistor of 6Ω, the amount of charge passing through it per second is...
[A] 90 C [B] 2/3 C [C] 2.5 C [D] 9 C
- If the resistance of a circuit is doubled and the applied potential difference is halved, the current passing through the circuit will ...
[A] become 1/4 of original [B] become 1/2 of original [C] become 4 times original [D] not change
- If the resistance of a circuit is halved and the applied potential difference is doubled, the current passing through the circuit will ...
[A] become 1/4 of original [B] become 1/2 of original [C] become 4 times original [D] not change
- A 200 m long wire has cross sectional area of 10-6 sq. m and its material has resistivity of 10-7Ω.m. What will be its resistance?
[A] 0.2Ω [B] 2Ω [C] 20Ω [D] 200Ω
- When two resistors with resistances R1 and R2 are connected in series and parallel, their equivalent resistances are R3 and R4, respectively. Then...
[A] R1R2 = R3R4 [B] R1R3 = R2R4 [C] R1R4 = R3R2 [D] R1R2R3R4 = 1
- When two resistors with resistance of 10Ω and 20Ω are connected in series with a 3 V battery, the current passing through the circuit will be...
[A] 0.1 A [B] 1 A [C] 2 A [D] 3 A
- When two resistors of 6Ω and 6Ω are connected in parallel with a 12V battery, the current flowing through the circuit is...
[A] 1.0 A [B] 2.0 A [C] 4.0 A [D] 0.25 A
- The kilowatt-hour is a unit of...
[A] electrical potential [B] electric power [C] electric energy [D] electric current
- 7.2 x 109 joule = _____ units of electrical energy.
[A] 0.2 [B] 20 [C] 2000 [D] 5000
- An electric lamp draws a current of 0.5 A when connected to a 9V battery. What is the power rating of the bulb?
[A] 4.5 W [B] 18 W [C] 41.5 W [D] 2.25 W
- If an electric iron has power rating of 2 kW, the cost of energy consumed for 24 hours at the rate of Rs. 6 per unit is equal to...
[A] Rs. 48 [B] Rs. 144 [C] Rs. 72 [D] Rs. 288
- How many joules of energy is transferred by an electric bulb of 60 W power rating in one minute?
[A] 60 [B] 1000 [C] 3600 [D] 6000
- A bulb has rating 12 V, 1 A. How much energy is consumed by it in 10 minutes?
[A] 120 J [B] 1200 J [C] 720 J [D] 7200 J
- Match the physical quantities in Part A with their units in Part B.
[A] 1-c, 2-a, 3-d, 4-b [B] 1-c, 2-b, 3-d, 4-a [C] 1-b, 2-d, 3-c, 4-a [D] 1-b, 2-a, 3-d, 4-c
- Match the physical quantity in Part A with formula in Part B.
[A] 1-c, 2-d, 3-a, 4-b [B] 1-b, 2-d, 3-a, 4-c [C] 1-b, 2-c, 3-d, 4-a [D] 1-c, 2-b, 3-a, 4-d
- Which of the following circuit symbol represents electric cell?
- Which of the following circuit symbol represents a resistor?
- What will be the equivalent resistance in the following circuit?
[A] 2 Ω [B] 3 Ω [C] 4 Ω [D] 6 Ω
- What will be the equivalent resistance between points A and b in the following circuit?
[A] 1 Ω [B] 2 Ω [C] 3 Ω [D] 4 Ω
- What will be the equivalent resistance between points A and b in the following circuit?
[A] 1 Ω [B] 2 Ω [C] 3 Ω [D] 4 Ω
- Which of the following circuits has the lowest equivalent resistance?
[A] Figure 1 [B] Figure 2 [C] Figure 3 [D] Figure 4
- Two resistors each of value R are connected in series in a circuit with V volt battery. If two more resistances each of magnitude R are connected in series in this circuit, the current in the circuit will...
[A] become double [B] become half [C] not change [D] become one fourth
- In an electric circuit, three bulbs of 40W, 60W and 100W are connected in series. The voltage drop is maximum across ____ bulb.
[A] 40W [B] 60W [C] 100W [D] None
- According to Ohm's law, voltage drop is inversely proportional to...
[A] I [B] 1/I [C] R [D] 1/R
- A 2 kW heater works on domestic voltage main supply. What should be the current rating of the fuse?
[A] 2 A [B] 5 A [C] 10 A [D] 6 A
- 6 C charge is passing through an electric bulb in one minute. How much current will pass through it?
[A] 10 A [B] 1 A [C] 0.1 A [D] 0.01 A
- On what does the heat produced in a resistance depend?
[A] Electric current passed [B] Resistance [C] Time for which current is passed [D] All of these
- The electric force between two charges, q1 and q2, is ______ proportional to the product of the magnitudes of the charges and _____ proportional to the square of the distance between them.
[A] directly, inversely [B] directly, directly [C] inversely, directly [D] inversely, inversely
- The resistance of a conductor is R. The resistance of another conductor of identical material and equal length with twice the diameter is...
[A] R/4 [B] R/2 [C] 2R [D] 4R
- Which of the following combinations of length(l) and cross-sectional area(A) will give a certain volume of copper the least resistance?
[A] l and A [B] 2l and A/2 [C] l/2 and 2A [D] none as the volume is same
- A resistor R1 dissipates power P when connected to a certain generator. If a resistor R2 is inserted in series with R1, the power dissipated by R1...
[A] decreases [B] increases [C] remains the same [D] any of the above depending on R1 and R2
- A resistor R1 dissipates power P when connected to a certain generator. If a resistor R2 is inserted in parallel with R1, the power dissipated by R1...
[A] decreases [B] increases [C] remains the same [D] any of the above depending on R1 and R2
- A 20-V potential difference is applied across a series combination of a 10 Ω and a 30 Ω resistors. The current in the 10 Ω resistor is...
[A] 0.5 A [B] 0.67 A [C] 1 A [D] 2 A
- Two identical resistors in parallel have an equivalent resistance of 2 Ω. If the resistors were in series, their equivalent resistance would be...
[A] 2 Ω [B] 4 Ω [C] 8 Ω [D] 16 Ω
- A 12-V potential difference is applied across a series combination of four 6Ω resistors. The current in each resistor is...
[A] 0.5A [B] 2A [C] 8A [D] 18A
- A 12-V potential difference is applied across a parallel combination of four 6Ω resistors. The current in each resistor is...
[A] 0.5A [B] 2A [C] 8A [D] 18A
- If a charge of Q coulomb flows in a part of a circuit across which there is a potential difference of V volt then the energy change W in joule is given by...
[A] Q.V [B] Q/V [C] V/Q [D] Q2/V
[A][B][C][D]
ANSWERS
(1) D (2) C (3) B (4) A (5) C (6) B (7) C (8) C (9) A (10) B (11) C (12) D (13) D (14) A (15) B (16) D (17) A (18) C (19) A (20) A (21) D (22) D (23) B (24) A (25) C (26) C (27) D (28) C (29) C (30) B (31) D (32) A (33) C (34) A (35) D (36) C (37) B (38) A (39) C (40) D (41) B (42) A (43) C (44) C (45) A (46) C (47) B (48) D (49) D (50) C (51) A (52) C (53) C (54) B (55) A (56) C (57) C (58) B (59) D (60) D (61) A (62) A (63) D (64) D (65) A (66) B (67) C (68) D (69) C (70) C (71) A (72) A (73) C (74) C (75) C (76) A (77) D (78) C (79) D (80) C (81) B (82) A (83) B (84) B (85) B (86) B (87) A (88) B (89) C (90) B (91) B (92) C (93) D (94) A (95) A (96) C (97) A (98) C (99) A (100) C (101) A (102) B (103) A